Brain and ENT Clinic – Dr Lalit Mahajan In Nagpur & Dr Rachna Gangwani Mahajan In Nagpur
Ear drum perforations
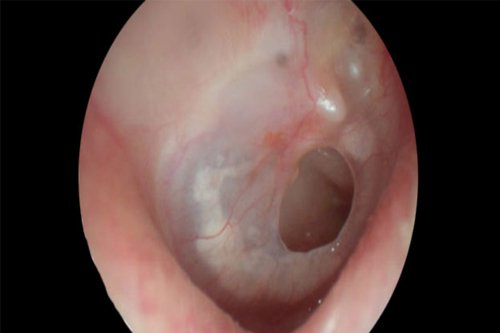
Causes of Ear Drum Perforations:
Infections: Severe ear infections, especially those with middle ear infections (otitis media), can lead to the accumulation of fluid or pus behind the ear drum, causing pressure that may result in a perforation.
Trauma: Injury to the ear, such as a direct blow to the ear, insertion of objects into the ear canal, or exposure to loud blasts or sudden changes in air pressure, can cause the ear drum to rupture.
Barotrauma: Rapid changes in air pressure, such as those experienced during air travel or scuba diving, can sometimes lead to ear drum perforations.
Foreign Objects: Inserting objects like cotton swabs or other items into the ear canal can cause injury to the ear drum.
Chronic Middle Ear Inflammation: Persistent inflammation in the middle ear, often associated with chronic ear infections or conditions like chronic otitis media, may lead to repeated ear drum perforations.
Symptoms of Ear Drum Perforations:
Ear Pain: Pain in the affected ear, especially during changes in pressure or when exposed to loud sounds.
Hearing Loss: Temporary hearing loss or a reduction in hearing sensitivity.
Ear Drainage: Fluid or pus may drain from the ear, especially if the perforation is associated with an infection.
Tinnitus: Ringing or buzzing sounds in the ear.
Vertigo: Some individuals may experience dizziness or a sensation of spinning.
Treatment of Ear Drum Perforations:
Observation and Monitoring:
- Small perforations may heal on their own without intervention. The healthcare provider may recommend regular check-ups to monitor the progress.
Medication:
- Antibiotics may be prescribed if there is an infection associated with the perforation.
Ear Drops:
- Ear drops may be used to prevent infection and promote healing.
Avoidance of Water Entry:
- It’s crucial to keep the ear dry to prevent infection. This may involve avoiding swimming or using ear protection when showering.
Surgery:
- In some cases, especially if the perforation is large or does not heal on its own, surgical repair (tympanoplasty) may be recommended to reconstruct the eardrum.
