Brain and ENT Clinic – Dr Lalit Mahajan In Nagpur & Dr Rachna Gangwani Mahajan In Nagpur
Ear Wax
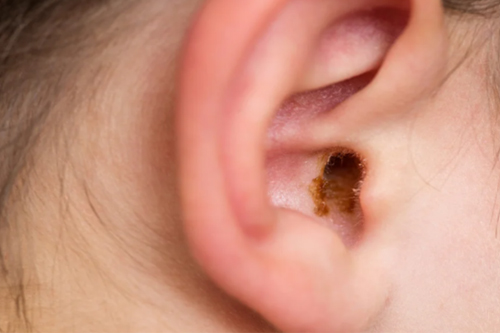
Symptoms of Ear Wax
Earache: Pain or discomfort in the ear can be a symptom of ear wax impaction.
Hearing loss: A partial blockage of the ear canal by ear wax can lead to decreased hearing or a sense of fullness in the ear.
Tinnitus: Ringing, buzzing, or other noises in the ear may be associated with ear wax buildup.
Dizziness or vertigo: In some cases, excessive ear wax can affect the balance organs in the inner ear, leading to dizziness or a spinning sensation.
Itching or drainage: Ear wax impaction may cause itching in the ear, and in some cases, there may be drainage or discharge.
Cough: Rarely, when ear wax stimulates the ear canal’s branch of the vagus nerve, it can lead to a reflex that causes coughing.
Treatment / Methods for Managing Ear Wax
Ear Drops:
- Over-the-counter ear drops are available to soften and loosen ear wax. These drops often contain mineral oil, hydrogen peroxide, or other ingredients designed to break down the wax.
Olive Oil:
- Warm olive oil can be used as a natural remedy to soften ear wax. Tilt your head to the side, and using an eyedropper, instill a few drops of lukewarm olive oil into the affected ear. Stay in that position for a few minutes to allow the oil to penetrate, and then drain the oil and softened wax by tilting your head in the opposite direction.
Hydrogen Peroxide:
- A mixture of equal parts hydrogen peroxide and water can be used to soften ear wax. Lie down on your side, and using an eyedropper, instill a few drops into the ear. Allow it to sit for a few minutes before draining it by tilting your head.
Ear Irrigation:
- Ear irrigation involves using a bulb syringe filled with warm water to gently flush out the ear wax. This method is often performed by a healthcare professional.
Manual Removal:
- In some cases, a healthcare provider may manually remove the ear wax using specialized tools. This is typically done if other methods are ineffective or if there is a significant blockage.
