Brain and ENT Clinic – Dr Lalit Mahajan In Nagpur & Dr Rachna Gangwani Mahajan In Nagpur
Electroencephalography (EEG) in Satna
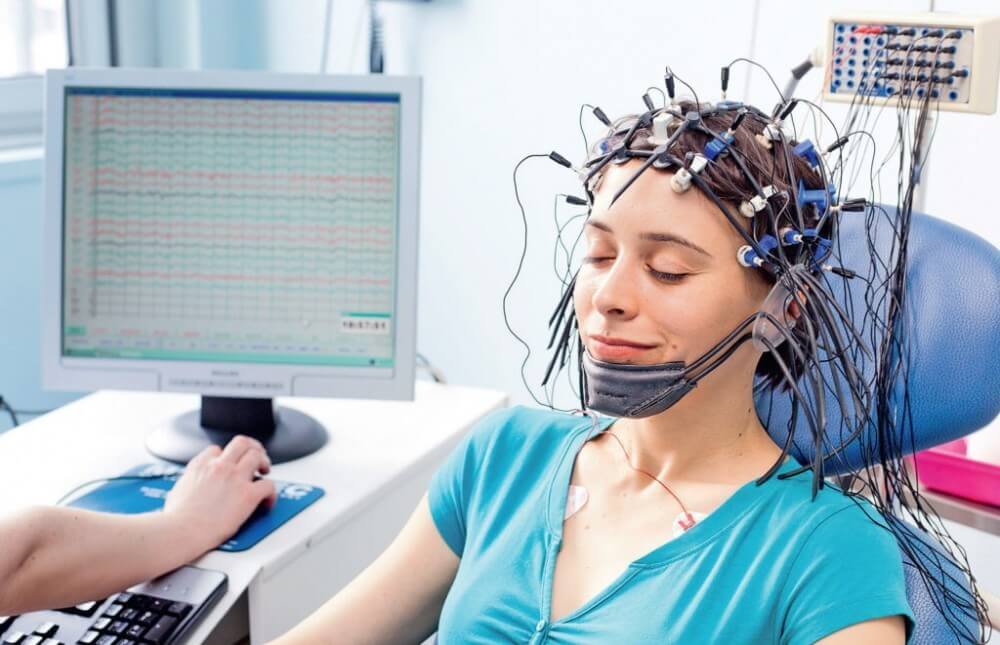
Electroencephalography (EEG) in Satna stands for electroencephalogram. It is a non-invasive neuroimaging technique that measures and records the electrical activity of the brain over time. The device use to record this activity is call an electroencephalograph.
EEG records the electrical activity generated by the firing of neurons in the brain. Neurons communicate with each other through electrical impulses, and this activity can be detect on the scalp.
EEG involves attaching small metal discs, known as electrodes, to the scalp. These electrodes are connect to an amplifier, and the resulting electrical signals are record and display as a series of wave patterns on a computer screen or paper.
EEG Symptoms
Seizures: Unexplained seizures or episodes of altered consciousness may be investigated using EEG. Thus, EEG can help identify abnormal electrical patterns associated with epilepsy.
Epilepsy: Individuals with a known history of epilepsy or those suspecte to have epilepsy may undergo EEG to monitor and characterize seizure activity.
Head Injuries: Once, If a person has experience a head injury and is exhibiting neurological symptoms or changes in behavior, EEG may be used to assess brain function.
Altered Mental Status: Thus, EEG can be helpful in cases where there is confusion, disorientation, or other changes in mental status without an apparent cause.
Sleep Disorders: EEG is commonly use in sleep studies to assess brain activity during different sleep stages. It can aid in the diagnosis of sleep disorders such as insomnia, sleep apnea, and parasomnias.
Monitoring Brain Function During Surgery: Firstly, In some cases, EEG is use to monitor brain function during certain types of surgeries, especially those that may involve the brain.
EEG procedure
Preparation:
- Before the EEG, the individual is usually advise to wash their hair thoroughly to remove any oils or products that may interfere with electrode contact.
- It’s essential to inform the healthcare provider about any medications the individual is taking, as certain medications can affect EEG results.
Electrode Placement:
- The person undergoing the EEG is typically seat in a comfortable chair or lying down on a bed. The scalp is then measure, and electrodes are strategically place on specific locations, typically base on the international 10-20 system for electrode placement.
- Electrode placement involves using a conductive gel to improve the contact between the electrodes and the scalp.
Recording Baseline Activity:
- The EEG recording often begins with the person at rest with their eyes close. This baseline recording helps establish normal brain activity.
Stimulus or Task Presentation (if need):
- Depending on the purpose of the EEG, the person may be asked to perform specific tasks or respond to stimuli during the recording. This can help researchers or clinicians study event-relate potentials and cognitive processes.
Recording Different States:
- The EEG may be record during different states, such as with eyes close, eyes open, and sometimes during specific sleep stages in sleep studies.
Recording Duration:
- A routine EEG typically lasts for about 20 to 45 minutes. However, longer recordings may be necessary for specific diagnostic purposes or to capture certain events, especially in the case of epilepsy monitoring.
Prevention EEG
Get a Good Night’s Sleep:
- Ensure you get a full night’s sleep before the test. Fatigue can affect the results.
Clean Hair:
- Wash your hair before the test, and avoid using hair products like gels, sprays, or conditioners, as they can interfere with the electrodes’ contact.
Avoid Stimulants:
- Limit or avoid stimulants like caffeine on the day of the test, as they can affect brain activity.
Inform the Technologist:
- Inform the EEG technologist about any medications you are taking and any specific health conditions or concerns you may have.
Comfortable Clothing:
- Wear comfortable clothing that allows easy access to your head and doesn’t interfere with electrode placement.
Relax:
- Try to stay relaxed during the test. It’s a painless procedure, and any movement or muscle tension can affect the EEG recording.
