Brain and ENT Clinic – Dr Lalit Mahajan In Nagpur & Dr Rachna Gangwani Mahajan In Nagpur
Seizures in Satna
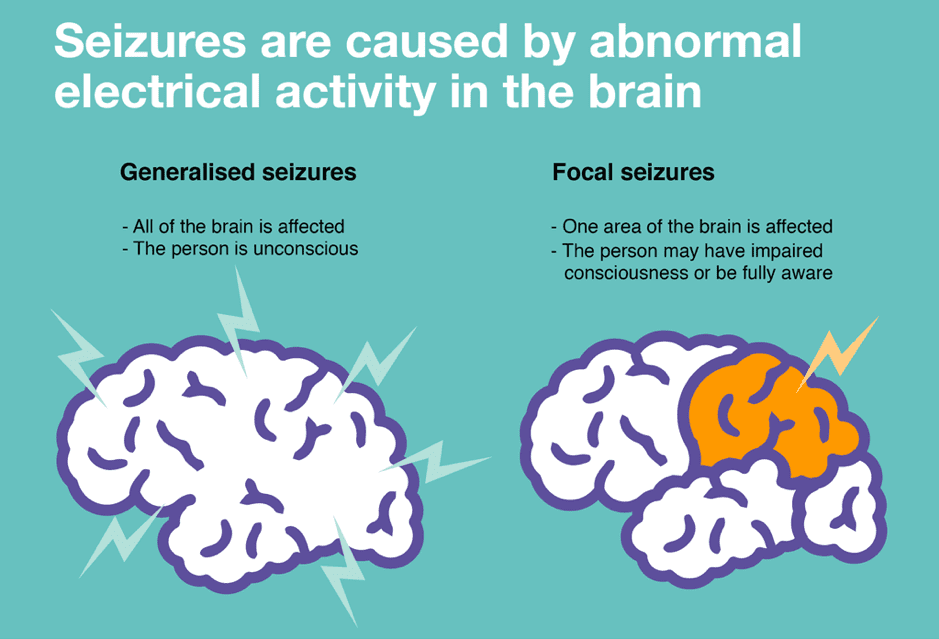
Seizures in Satna are sudden, uncontrolled electrical disturbances in the brain that can manifest in various ways. From brief lapses in awareness to full-body convulsions, seizures can be frightening. However, with the right knowledge and care, individuals with seizures can lead fulfilling lives.
Seizures in Satna comes with its unique challenges, but with the right medical support and local resources, you can effectively manage the condition.
Whether you’re seeking expert medical advice, connecting with others in the community, or staying inform about the latest advancements, Satna has the resources you need for comprehensive seizure care.
Symptoms Seizures
Absence Seizures:
- Brief Loss of Consciousness: Typically lasts for a few seconds.
- Blank Stare: The person may appear to be staring into space and may not be aware of their surroundings.
Tonic Seizures:
- Muscle Stiffening: Involves sudden and stiffening of muscles.
- Loss of Consciousness: Often leads to a brief loss of consciousness and may cause falls.
Clonic Seizures:
- Rhythmic Movements: Characterize by rhythmic, jerking muscle movements.
- Loss of Consciousness: Can be associate with a loss of consciousness.
Myoclonic Seizures:
- Brief, Jerking Movements: Involves quick, involuntary muscle jerks.
- No Loss of Consciousness: Consciousness is typically maintain.
Tonic-Clonic Seizures (formerly Grand Mal Seizures):
- Tonic Phase: Involves stiffening of muscles.
- Clonic Phase: Follow by rhythmic, jerking movements.
- Loss of Consciousness: Often results in a loss of consciousness.
Atonic Seizures:
- Loss of Muscle Tone: Involves a sudden loss of muscle strength and may cause a person to collapse.
- Brief Loss of Consciousness: Can be associate with a brief loss of consciousness.
Treatment Seizures
Antiepileptic Medications:
- The primary and most common treatment for seizures involves the use of antiepileptic medications (also known as anticonvulsants). These medications aim to control or prevent seizures.
- The specific medication prescribed will depend on the type of seizures, the individual’s age, overall health, and any potential side effects.
- Examples of antiepileptic medications include phenytoin, carbamazepine, valproic acid, levetiracetam, lamotrigine, and many others.
Ketogenic Diet:
- The ketogenic diet is a high-fat, low-carbohydrate diet that has been shown to be effective in some cases, especially in children with difficult-to-control seizures.
- This diet can be used under the supervision of a healthcare team, typically including a dietitian.
Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS):
- Vagus nerve stimulation involves implanting a device under the skin that stimulates the vagus nerve. This may help reduce the frequency and severity of seizures.
- It is often consider for individuals with epilepsy that is not well-controll with medications.
Responsive Neurostimulation (RNS):
- Responsive neurostimulation is a newer treatment option where a device is implanted in the brain to detect and respond to abnormal electrical activity, potentially preventing seizures.
Surgery:
- In cases where seizures originate from a specific area of the brain that can be identify and safely remove, surgery may be consider.
- Thus, This option is usually explore after careful evaluation, including neuroimaging and other diagnostic tests.
Lifestyle Modifications:
- Firstly, Ensuring a regular sleep schedule, managing stress, and avoiding known triggers can be important in managing seizures.
- once. Alcohol and drug avoidance is crucial, as these substances can lower the seizure threshold.
Avoiding Triggers:
- Thus, Identifying and avoiding specific triggers that may precipitate seizures, such as lack of sleep, stress, or certain medications.
